Pentacube Oddities with Diagonal Mirror Symmetry
Introduction
A pentacube is a solid made of five cubes joined
face to face.
An oddity (or Sillke Figure)
is a figure with even symmetry
formed by an odd number of copies of a polyform.
In 1996, Torsten Sillke reported
having found a point-symmetric arrangement of 17 F pentacubes.
He asked whether 17 is the least such odd number,
and more generally whether an odd number of copies of a polycube can be arranged
to achieve any given symmetry.
This was the earliest known mention of polyform oddities.
Polycubes have 33 symmetry classes (including asymmetry),
and 31 of them have even order.
That is too many to show here.
Instead I show only oddities with diagonal mirror symmetry.
In all pictures, the cross-sections are shown from top to bottom.
If you find a smaller solution, please write.
For other classes of symmetry, see:
Diagonal Mirror Symmetry
Diagonal mirror symmetry is the symmetry of reflection
through a plane parallel to the plane through some pairs of opposite edges
of cells.
The smallest example of a polycube with diagonal mirror
symmetry and no stronger symmetry
is the K pentacube, as found by W. F. Lunnon:

Achiral Pentacubes
The solutions for pentacubes
A,
I,
K,
M,
Q,
V,
W,
and
X
are trivial.
Those pentacubes already have diagonal mirror symmetry.
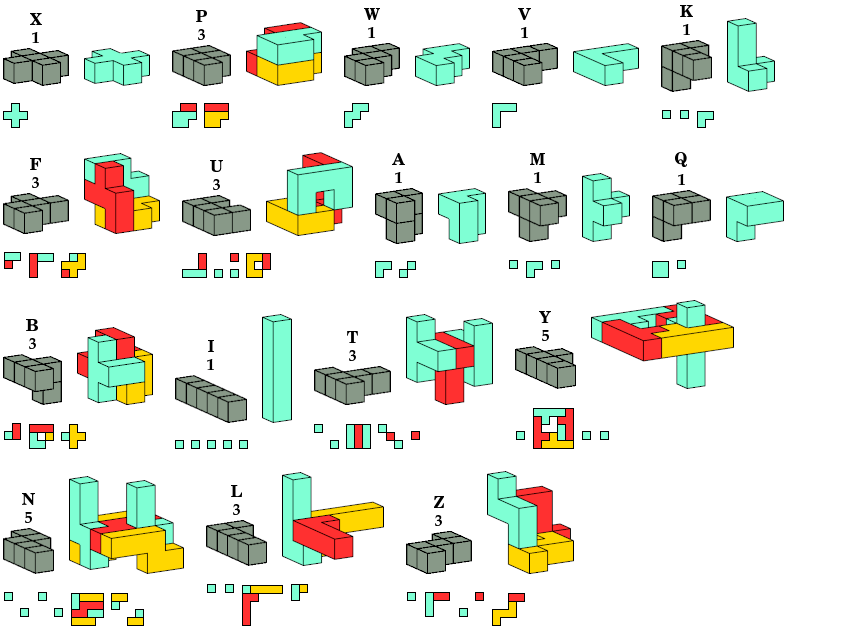
Chiral, Disallowing Reflection
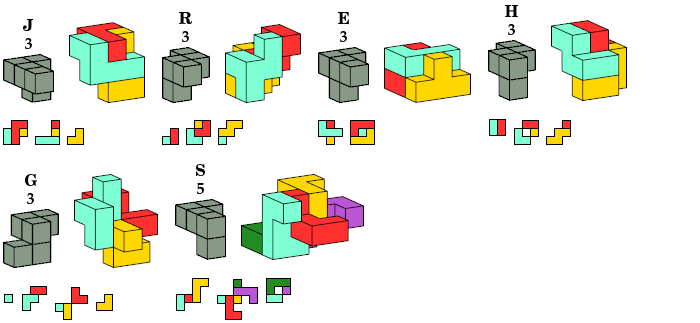
Chiral, Allowing Reflection
Last revised 2024-01-27.
Back to Polyform Oddities
<
Polyform Curiosities
Col. George Sicherman
[ HOME
| MAIL
]




